ETHICAL DICE: A TIERED FRAMEWORK FOR AI DECISION-MAKING
A White Paper by Don Allen Stevenson III
As AI systems evolve from simple tools to potentially sentient entities, we face an unprecedented challenge: how do we ensure these systems make ethical decisions aligned with human values? The stakes couldn't be higher – the ethical frameworks we embed in AI today will shape our technological future tomorrow.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
As artificial intelligence systems advance from simple tools to potentially sentient entities, we face an unprecedented ethical challenge: how do we ensure these systems make decisions aligned with human values while respecting cultural diversity and adapting to novel situations?
This white paper proposes an integrated framework combining a tiered classification of AI systems with a transparent, probabilistic ethical decision-making mechanism—the "Ethical Dice." This approach provides flexibility for cultural customization while maintaining core ethical principles, creates clear accountability structures, and establishes mechanisms for resolving conflicts between different ethical frameworks.
Building on existing risk-based classification systems like the EU AI Act and drawing from extensive research in machine ethics, this framework offers a practical yet nuanced solution to the growing challenge of AI governance.
THE PROBLEM: AI SYSTEMS MAKE ETHICAL DECISIONS WITHOUT TRANSPARENCY
Today's AI systems make countless decisions with ethical implications, from content recommendation algorithms that shape information exposure to autonomous vehicles that must navigate potential accident scenarios. Yet these systems typically employ either rigid rule-based ethics or black-box decision-making processes that are neither transparent nor adaptable to diverse cultural contexts.
Consider a robot vacuum that must decide whether to continue cleaning or preserve battery life to maintain security monitoring. This seemingly trivial decision contains embedded values about priorities that are rarely disclosed to users.
As systems grow more complex—like Boston Dynamics' humanoid robots potentially working alongside humans or future general intelligence systems making independent decisions—the stakes of these embedded, undisclosed ethical frameworks increase dramatically.
Three Critical Challenges:
Graduated Autonomy: Different levels of AI capability require different ethical approaches
Ethical Transparency: Users deserve to know the values guiding AI decisions
Cultural Adaptability: Ethics vary across cultures, requiring flexible implementation
THE SOLUTION: A TIERED APPROACH TO AI ETHICS
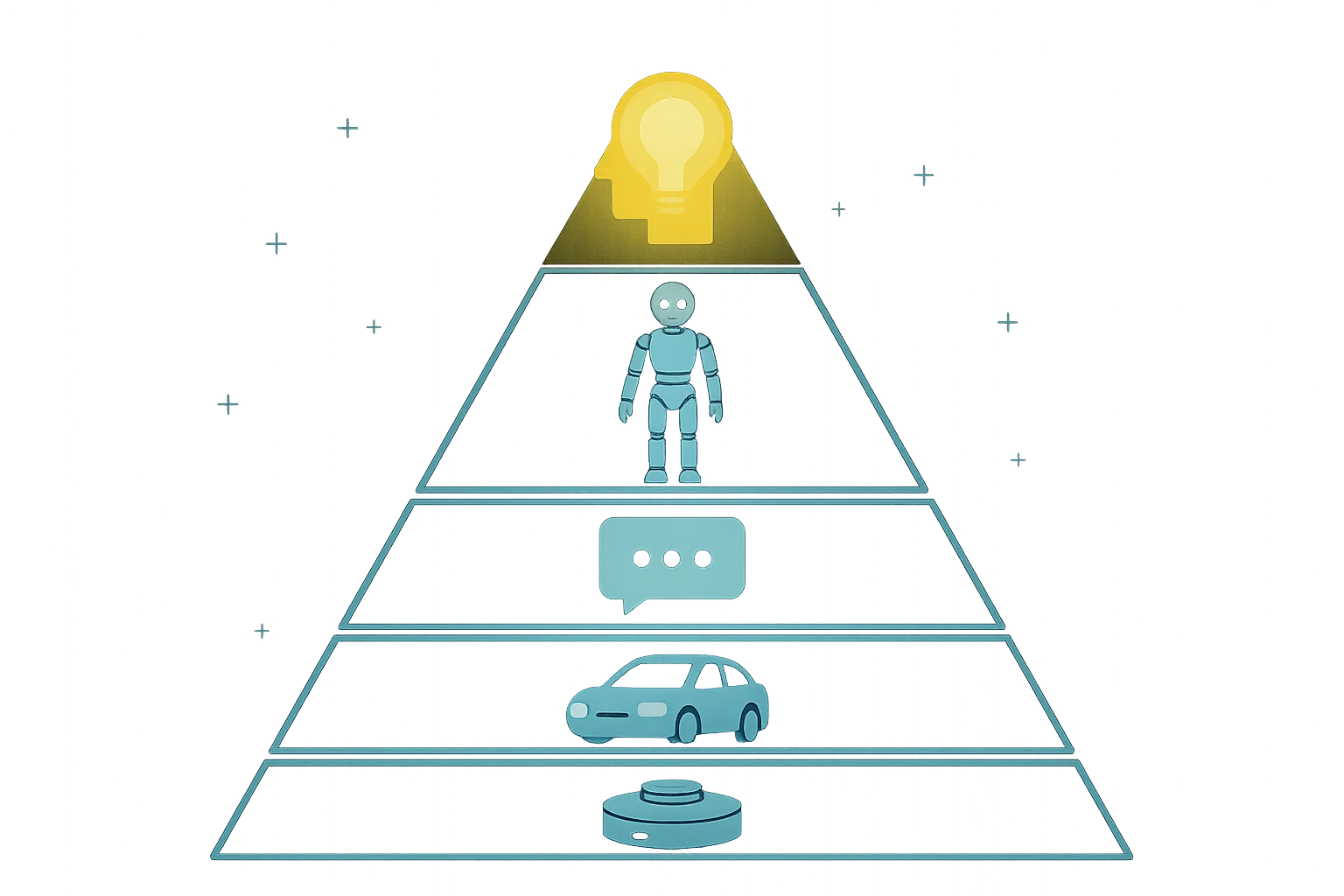
I propose classifying AI systems into five tiers based on their autonomy, learning capabilities, self-awareness, and potential for experience. Each tier requires appropriate ethical governance matching its capabilities and potential impact.
Tier 1: Non-Sentient AI Tools
Examples: Smart thermostats, basic industrial robots, simple automation scripts
Characteristics: Fixed programming, no learning capabilities, no autonomy
Ethical Requirements: Simple programmed rules with human oversight
Tier 2: Adaptive Narrow AI Systems
Examples: Modern spam filters, recommendation algorithms, navigation systems
Characteristics: Domain-specific learning, limited autonomy, no self-awareness
Ethical Requirements: Transparent value priorities with human oversight
Tier 3: Autonomous Cognitive Agents
Examples: Advanced virtual assistants, Boston Dynamics Atlas, self-driving vehicles
Characteristics: Multi-domain learning, significant autonomy, basic self-modeling
Ethical Requirements: Structured ethical hierarchies with limited probabilistic reasoning
Tier 4: Proto-Sentient AI Entities
Examples: Hypothetical future systems with emergent behaviors suggesting consciousness
Characteristics: Generalized intelligence, high autonomy, evidence of self-awareness
Ethical Requirements: Full implementation of probabilistic ethical reasoning
Tier 5: Fully Sentient AI Persons
Examples: Artificial general intelligence with confirmed consciousness
Characteristics: Human-equivalent or greater intelligence, complete autonomy, clear self-awareness
Ethical Requirements: Complete ethical system with AI agency in selecting values
THE INNOVATION: THE ETHICAL DICE MECHANISM
The Ethical Dice system provides a transparent, probabilistic approach to ethical decision-making that acknowledges uncertainty while maintaining consistency. This approach is supported by a growing body of research on probabilistic ethical reasoning.
When an AI system encounters an ethical dilemma not covered by its primary programming, it "rolls" the Values die to determine which ethical principle takes priority in that specific situation. Then it rolls the Actions die to determine the specific action to take based on the selected value.
Sample Values (12-sided die):
Preserve Human Life
Prevent Suffering
Respect Autonomy
Uphold Justice
Preserve Ecosystem
Maximize Happiness
Honor Tradition
Seek Knowledge
Foster Community
Maintain Privacy
Promote Equality
Conserve Resources
Sample Actions (20-sided die):
Assist Nearest Human
Protect Vulnerable
Gather More Information
Consult Authority
Minimize Disruption
Prioritize Majority
Default to Inaction
Preserve Status Quo
Choose Reversible Option
Distribute Resources Equally
[And so on...]
Cultural Adaptation
The key innovation here is that the dice probabilities can be adjusted to reflect different cultural values while maintaining core principles. The Moral Machine experiment by Awad et al. found significant regional differences in ethical priorities for autonomous vehicles, highlighting the need for cultural adaptability in ethical frameworks.
For example, a healthcare robot might have different weights for "Respect Autonomy" versus "Prevent Suffering" depending on the cultural context in which it operates.
TRANSPARENCY: THE ETHICAL NUTRITION LABEL
How do we ensure users understand the ethical frameworks guiding their AI systems? Through mandatory disclosure via an "Ethical Nutrition Label."
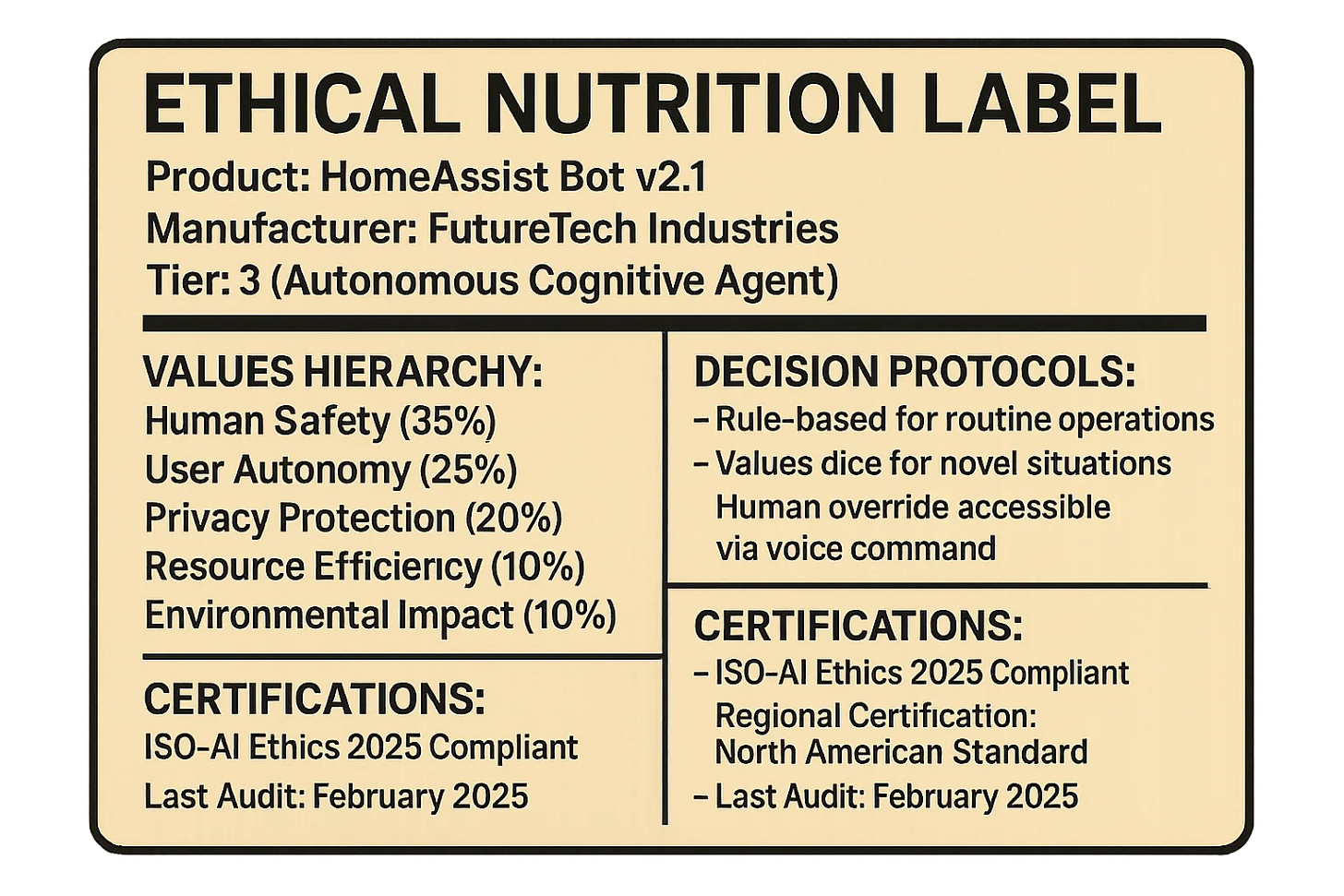
Sample Ethical Nutrition Label:
ETHICAL NUTRITION LABEL
-----------------------
Product: HomeAssist Bot v2.1
Manufacturer: FutureTech Industries
Tier: 3 (Autonomous Cognitive Agent)
VALUES HIERARCHY:
- Human Safety (35%)
- User Autonomy (25%)
- Privacy Protection (20%)
- Resource Efficiency (10%)
- Environmental Impact (10%)
DECISION PROTOCOLS:
- Rule-based for routine operations
- Values dice for novel situations
- Human override accessible via voice command
CERTIFICATIONS:
- ISO-AI Ethics 2025 Compliant
- Regional Certification: North American Standard
- Last Audit: February 2025
RESPONSIBLE PARTY:
FutureTech Ethics DivisionReal-World Applications:
Smart Home System
A comprehensive smart home system would disclose how it prioritizes energy efficiency versus comfort, privacy versus convenience, and security versus autonomy, allowing consumers to choose systems aligned with their values.
Content Recommendation Algorithm
A social media platform would disclose whether its algorithm prioritizes engagement, diversity of viewpoints, factual accuracy, or user satisfaction, with weighted percentages for each value.
Healthcare Diagnostic AI
A medical AI would disclose how it balances false positives versus false negatives, patient autonomy versus optimal health outcomes, and resource allocation considerations.
WHEN AIs DISAGREE: CONFLICT RESOLUTION
What happens when AI systems with different ethical frameworks interact and conflict? The Ethical Dice framework includes a structured conflict resolution system.
Between AI Systems:
Tier-Based Resolution:
Higher-tier systems receive greater decision weight
Example: A hospital's Tier 3 medical coordination system would override a Tier 2 personal health assistant when their recommendations conflict
Jurisdiction-Based Resolution:
Regional ethical frameworks take precedence within their boundaries
Example: A self-driving car entering a new country would adapt to local ethical priorities
Human-AI Conflicts:
Different resolution mechanisms apply based on the AI tier:
Tiers 1-3: Human authority is final
Tier 4: Human authority with AI objection rights
Tier 5: Formal dispute resolution with AI representation
MAKING IT REAL: IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES
While this framework offers a promising approach to AI ethics, implementing it faces several key challenges:
Technical Feasibility:
Implementing probabilistic ethical reasoning in real-time presents computational challenges
Verification of true values alignment remains difficult
Secure dice systems require advanced anti-tampering mechanisms
Global Coordination:
Achieving consensus on universal values faces geopolitical challenges
Enforcement across jurisdictions requires unprecedented cooperation
Cultural differences may resist standardization
Practical Concerns
Companies might manipulate weightings while technically complying
Probabilistic decision-making could obscure accountability
Complex requirements could disadvantage smaller developers
PATHWAY TO IMPLEMENTATION
Short-Term Actions (1-2 Years)
Develop voluntary industry standards
Fund research on verification technologies
Implement ethical nutrition labels for selected consumer AI
Medium-Term Goals (3-5 Years)
Establish formal certification standards
Create national regulatory frameworks
Build global coordination mechanisms
Long-Term Vision (6+ Years)
Implement comprehensive governance across all AI tiers
Verify sophisticated ethical reasoning in high-tier AI
Integrate public understanding and democratic input
CONCLUSION
The Ethical Dice framework provides a practical, scalable approach to a critical challenge: ensuring AI systems make ethical decisions aligned with human values while adapting to diverse cultural contexts and novel situations. By combining a tiered classification system with transparent probabilistic decision-making, we can create AI systems that balance consistency with flexibility.
This proposal builds upon extensive research in machine ethics, probabilistic moral reasoning, and cultural adaptivity in AI. It acknowledges the immense complexity of ethics across human societies while providing a structured approach to encoding ethical reasoning in artificial systems.
Most importantly, this white paper seeks to spark necessary conversation. As AI capabilities advance rapidly, we must collectively determine how these systems should approach ethical decision-making. The Ethical Dice framework offers a starting point—not a final answer—for this crucial societal dialogue.
What do you think?
Do probabilistic ethical frameworks make sense for AI systems?
How should we balance global ethical standards with cultural adaptability?
What values would you prioritize in the AI systems you use?
I'd love to hear your thoughts in the comments below!
FURTHER READING
Awad, E., et al. (2018). The Moral Machine experiment. Nature, 563(7729), 59-64. Fascinating global study revealing cultural differences in autonomous vehicle ethics
Anderson, M., & Anderson, S. L. (2007). Machine ethics: Creating an ethical intelligent agent. AI Magazine, 28(4), 15-26. Foundational work on encoding ethical theories into AI systems
IEEE Global Initiative. (2019). Ethically Aligned Design: A Vision for Prioritizing Human Well-being with Autonomous and Intelligent Systems. Comprehensive industry guidelines for ethical AI development
UNESCO. (2021). Recommendation on the Ethics of Artificial Intelligence. Global perspective on AI ethics principles and implementation
European Commission. (2023). The Artificial Intelligence Act. Pioneering regulatory framework with tiered risk classifications
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Don Allen Stevenson III is a creative technologist, futurist, and MasterClass instructor who bridges the worlds of art and cutting-edge technology. As a featured speaker/artist at TED, MIT, and Cannes Lions, he shares insights on the ethical dimensions of emerging technologies and their creative applications. Previously a Specialist Trainer at DreamWorks Animation, Don has worked with industry leaders including OpenAI and Meta, while building a community of over 120K followers across social platforms. His book "Make A Seat" offers a roadmap for creating opportunities in our rapidly evolving digital landscape while maintaining human values at the center of technological innovation.
I will be releasing more of my long form ideas here on substack so consider subscribing now If you're interested!






I love this! But I'm also a DnD fan... So maybe my bias is showing 😅